Understanding and Addressing Common Nutritional Deficiencies in Cannabis Cultivation
Introduction:
Cannabis cultivation is a complex process that requires meticulous attention to various factors to ensure a successful and healthy harvest. One critical aspect often overlooked is the nutritional needs of the cannabis plant. Nutrient deficiencies can significantly impact the growth, development, and overall yield of cannabis crops. In this article, we will delve into the most common nutritional deficiencies encountered in cannabis cultivation and explore effective strategies to address them.
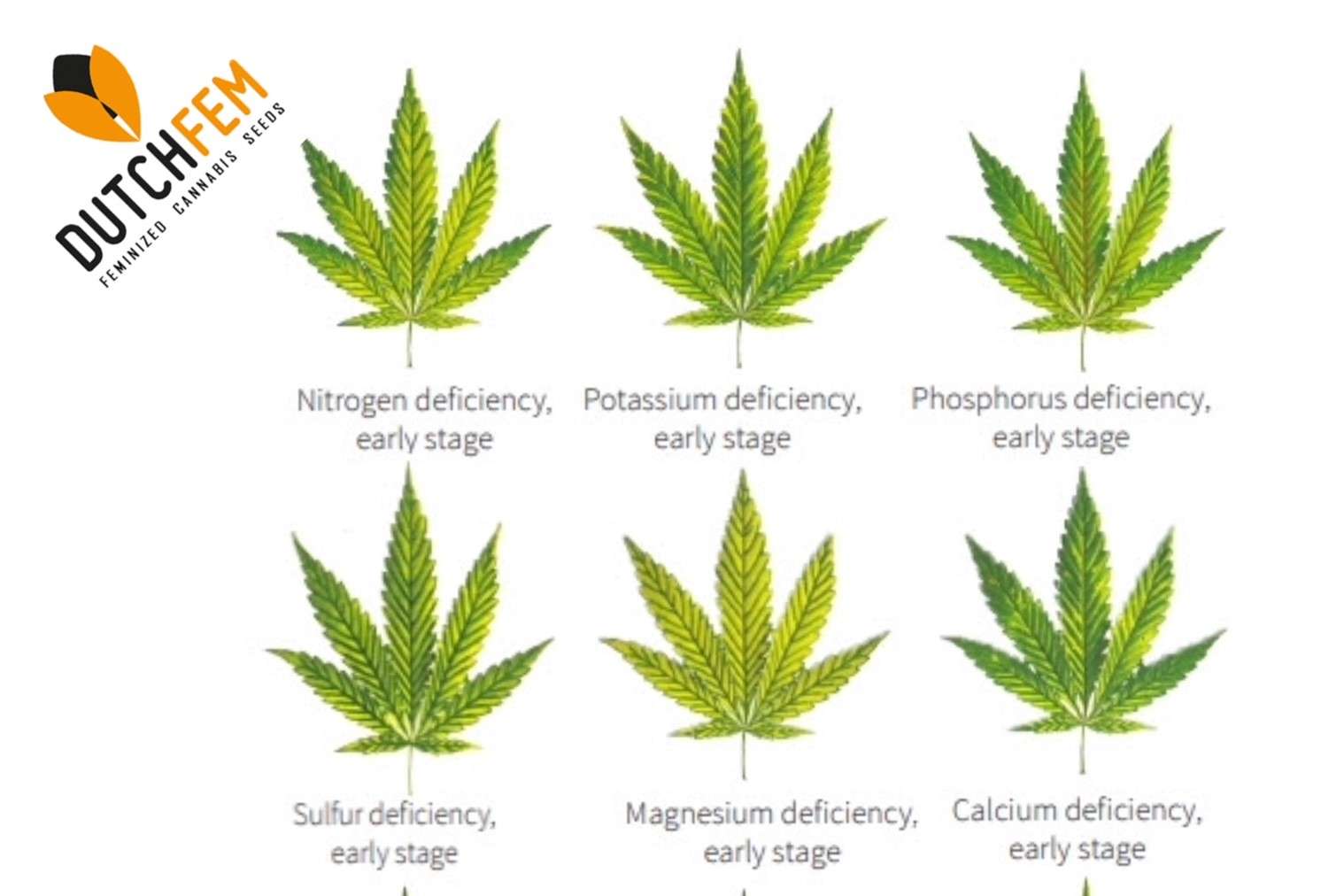
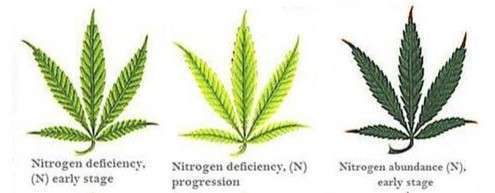
Nitrogen Deficiency:
Nitrogen is a fundamental element required for the synthesis of proteins, enzymes, and chlorophyll, all of which play crucial roles in plant growth. Nitrogen deficiency is a common issue in cannabis cultivation, leading to stunted growth, yellowing of older leaves, and a general decline in plant vigor. To address nitrogen deficiency, cultivators can incorporate nitrogen-rich fertilizers or organic amendments into their nutrient regimen. It’s important to strike a balance, as excessive nitrogen can lead to other issues, such as delayed flowering.
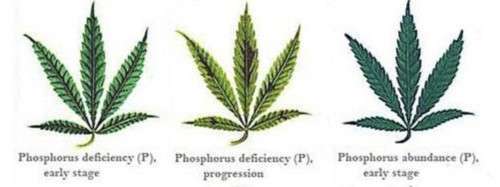
Phosphorus Deficiency:
Phosphorus is essential for energy transfer and storage, cell division, and the overall development of roots and flowers. A lack of phosphorus can manifest as dark green leaves, slow growth, and a delay in flowering. Cultivators should ensure that their nutrient mix includes an adequate amount of phosphorus, especially during the flowering stage. Additionally, adjusting the pH level of the growing medium can enhance phosphorus uptake.
Potassium is crucial for the activation of enzymes, water uptake, and the transportation of nutrients within the plant. Deficiency symptoms include yellowing at the leaf edges, weak stems, and reduced resistance to pests and diseases. Cultivators should provide a balanced fertilizer containing potassium and monitor pH levels to optimize nutrient absorption.
Magnesium Deficiency:
Magnesium is an essential component of chlorophyll and is vital for photosynthesis. A lack of magnesium often results in yellowing between leaf veins, resembling an interveinal chlorosis. To rectify magnesium deficiency, cultivators can apply magnesium-containing fertilizers or foliar sprays. It’s important to maintain the correct pH range for optimal magnesium absorption.
Calcium Deficiency:
Calcium is crucial for cell wall structure, root development, and nutrient transport. A calcium deficiency can lead to distorted growth, weak stems, and blossom end rot in flowers. Cultivators can address this issue by using calcium-rich fertilizers or supplements. Additionally, maintaining proper pH levels is essential for calcium availability.
Iron Deficiency:
Iron is essential for chlorophyll production and overall plant health. Symptoms of iron deficiency include yellowing between leaf veins, but with distinct green veins. Adjusting the pH of the growing medium and using iron chelates or foliar sprays can help alleviate this deficiency.

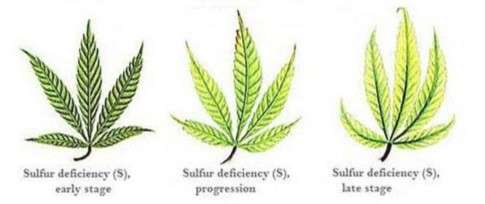
Sulfur is a component of amino acids and is essential for protein synthesis. Sulfur deficiency manifests as yellowing of younger leaves and can stunt plant growth. Adding sulfur-containing fertilizers or amendments can correct this deficiency, but careful monitoring is necessary to avoid excessive sulfur levels.
Zinc Deficiency:
Zinc is crucial for enzyme activation and hormone synthesis. A deficiency can lead to distorted leaves with yellowing between veins. Correcting zinc deficiency involves applying zinc-containing fertilizers or foliar sprays. However, excess zinc can be toxic, so it’s important to maintain a balanced approach.

Achieving a successful cannabis harvest requires a comprehensive understanding of the plant’s nutritional needs. Nutrient deficiencies can significantly impact growth, yield, and the overall quality of the final product. Cultivators must monitor their plants closely, recognize deficiency symptoms, and take prompt corrective measures. Additionally, maintaining the proper pH level of the growing medium is crucial for nutrient absorption.
By addressing common nutritional deficiencies through appropriate fertilization and cultivation practices, cannabis cultivators can optimize plant health, maximize yields, and produce high-quality crops. Regular soil testing, proper nutrient management, and a proactive approach to addressing deficiencies are essential elements of successful cannabis cultivation.



















































You must be logged in to post a comment.