The Importance of pH in Cannabis Cultivation
pH, or potential hydrogen, stands as a fundamental factor in the successful cultivation of cannabis plants. This measure of acidity or alkalinity profoundly influences various aspects of plant health, including nutrient availability, microbial activity, and overall growth vigor. Understanding the significance of pH and its impact on cannabis cultivation is paramount for achieving desirable yields and quality harvests.
Nutrient Availability:
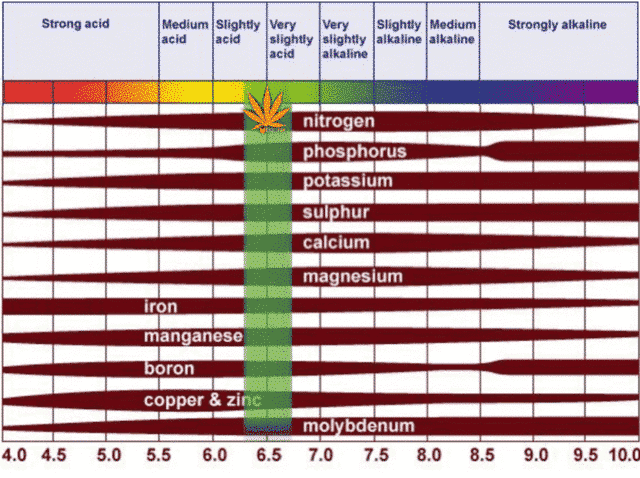
One of the primary roles of pH in cannabis cultivation is its effect on nutrient availability within the growing medium. pH levels that stray too far from the optimal range can lead to nutrient imbalances or deficiencies, hindering the plant’s ability to uptake essential elements. When pH levels are too high (alkaline) or too low (acidic), certain nutrients become chemically bound in the soil or substrate, rendering them inaccessible to the plant’s root system. This phenomenon, known as nutrient lockout, results in stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and overall poor plant health.
By maintaining the correct pH level, growers ensure that nutrients remain in a soluble form, readily available for uptake by the plant. This allows cannabis plants to access the essential elements they need for healthy growth, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and various micronutrients. Achieving optimal nutrient availability through proper pH management is essential for promoting robust vegetative growth, maximizing flowering potential, and ultimately, enhancing overall crop yields.
Microbial Activity:
pH also plays a pivotal role in influencing microbial activity within the soil or substrate. Beneficial microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and mycorrhizal fungi, form symbiotic relationships with cannabis roots, aiding in nutrient uptake, disease resistance, and overall plant health. These microorganisms thrive in specific pH ranges, and deviations from these optimal conditions can disrupt their activity and negatively impact plant performance.
In acidic soils or substrates with low pH levels, beneficial microbial populations may struggle to thrive, leading to reduced nutrient cycling and impaired root colonization. Conversely, excessively alkaline conditions can inhibit microbial activity and alter the microbial community composition, potentially increasing the risk of pathogen proliferation. By maintaining the correct pH range conducive to microbial activity, growers create an environment that supports a diverse and flourishing microbial ecosystem, enhancing nutrient availability and plant resilience.
In conclusion, pH serves as a critical determinant of success in cannabis cultivation, influencing nutrient availability, microbial activity, and overall plant health. By maintaining the correct pH level within the optimal range for the chosen growing medium, growers can ensure that their cannabis plants have access to essential nutrients, foster beneficial microbial communities, and thrive throughout the cultivation cycle. In the following sections, we will delve into the ideal pH ranges for different growing mediums, including soil, coco coir, and hydroponic systems like rockwool, and discuss practical strategies for pH management in each setting.
The Importance of pH in Cannabis Cultivation – Ideal PH Levels:
Soil:
When cultivating cannabis in soil, achieving and maintaining the correct pH level is crucial for optimal plant growth and development. The ideal pH range for soil-based cultivation typically falls between 6.0 and 7.0. Within this range, cannabis plants can efficiently absorb essential nutrients, promoting vigorous growth and robust flowering.
Soil pH levels outside of the recommended range can significantly impact nutrient availability and uptake. In acidic soils with pH levels below 6.0, certain nutrients such as phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium may become less available to the plant, leading to deficiencies and diminished growth. Conversely, alkaline soils with pH levels above 7.0 can result in nutrient imbalances and toxicity, as well as hinder the uptake of micronutrients like iron and manganese.
To ensure optimal soil pH levels for cannabis cultivation, growers should regularly monitor and adjust pH as needed. This can be achieved through the use of pH testing kits or meters, which provide accurate measurements of soil acidity or alkalinity. If pH levels deviate from the ideal range, corrective measures can be taken using pH-adjusting products or natural amendments.
One commonly used amendment for raising soil pH is dolomite lime, which contains calcium and magnesium carbonates that help neutralize acidity. Incorporating dolomite lime into the soil mix or applying it as a top dressing can gradually raise pH levels and improve nutrient availability. Conversely, acidic soils can be buffered using materials such as agricultural lime or gypsum to lower pH and create a more favorable growing environment.
By maintaining the correct pH level in soil, cannabis growers can ensure optimal nutrient uptake, microbial activity, and overall plant health. Regular monitoring and adjustment of pH levels throughout the cultivation cycle are essential for maximizing yields and producing high-quality cannabis crops. In the following sections, we will explore the ideal pH ranges for other popular growing mediums, including coco coir and hydroponic systems like rockwool, and discuss best practices for pH management in each setting.
Coco Coir:
Coco coir, renowned for its excellent water retention and aeration properties, has gained popularity as a growing medium for cannabis cultivation. However, due to its unique composition, coco coir requires specific pH considerations to support optimal plant growth.
The ideal pH range for coco coir cultivation typically falls between 5.5 and 6.5. This slightly acidic to neutral pH range allows cannabis plants to efficiently uptake nutrients while minimizing the risk of nutrient imbalances or deficiencies. Coco coir naturally tends to have a slightly acidic pH, so maintaining pH levels within the recommended range is crucial for preventing nutrient lockout and ensuring robust plant development.
To achieve and maintain the desired pH range in coco coir, growers should regularly monitor pH levels using a reliable pH meter or testing kit. If pH levels deviate from the optimal range, adjustments can be made using pH-stabilizing solutions or buffering agents specifically designed for use with coco coir. These products help regulate pH levels and ensure that nutrient uptake remains unhindered, promoting healthy root development and vigorous growth.

Hydroponics (Rockwool):
In hydroponic systems utilizing inert substrates like rockwool, precise pH control is essential for facilitating nutrient uptake and maximizing plant performance. Rockwool, a popular choice among hydroponic growers, provides excellent support for cannabis roots and allows for efficient nutrient delivery. However, maintaining the correct pH level is crucial to prevent nutrient imbalances and ensure optimal nutrient availability.
The ideal pH range for hydroponic cultivation in rockwool typically ranges between 5.5 and 6.5, similar to coco coir. This pH range allows cannabis plants to effectively absorb nutrients while minimizing the risk of nutrient deficiencies or toxicities. By closely monitoring pH levels and making necessary adjustments, growers can create an optimal growing environment that promotes healthy root development and robust growth in hydroponic systems.
To maintain pH levels within the desired range in hydroponic systems, growers should utilize pH meters or monitoring devices to regularly measure pH levels in the nutrient solution. pH-adjusting solutions or acids/bases can be used to raise or lower pH as needed, ensuring that nutrient uptake remains optimized for healthy cannabis growth.
In summary, maintaining the correct pH level is crucial for successful cannabis cultivation in both coco coir and hydroponic systems like rockwool. By understanding the ideal pH ranges for each growing medium and implementing proper pH management techniques, growers can optimize nutrient uptake, promote vigorous growth, and achieve impressive yields in their cannabis crops.

Adding nutrients to water before adjusting pH is a standard practice in cannabis cultivation, and there are several reasons why it’s important to follow this sequence:
Nutrient Stability: Mixing nutrients into water before adjusting pH allows for better stability of the nutrient solution. Some nutrients can undergo chemical reactions or precipitation when pH levels are altered. By first dissolving the nutrients in water, they have a chance to stabilize before pH adjustments are made, reducing the risk of nutrient precipitation or nutrient lockout.
Accurate pH Adjustment: Adjusting pH after adding nutrients ensures more accurate pH readings and adjustments. Nutrients can influence the pH of the solution, so attempting to adjust pH before adding nutrients may result in inaccurate readings. By adding nutrients first, growers can accurately measure and adjust pH levels to the desired range for optimal nutrient uptake by cannabis plants.
Preventing pH Drift: pH drift, or the gradual change in pH over time, is a common issue in nutrient solutions. When nutrients are added to water first, pH adjustments can be made to stabilize the solution within the desired pH range. This helps prevent pH drift and ensures that the nutrient solution maintains optimal pH levels for the duration of the growing cycle.
Maximizing Nutrient Uptake: Correct pH levels are essential for maximizing nutrient uptake by cannabis plants. Cannabis plants have specific pH preferences for nutrient absorption, and maintaining pH within the optimal range ensures that nutrients remain available and accessible to the plant’s root system. By adding nutrients first and then adjusting pH, growers can create an environment conducive to efficient nutrient uptake and healthy plant growth.
In summary, adding nutrients to water before adjusting pH is important for maintaining nutrient stability, achieving accurate pH readings, preventing pH drift, and maximizing nutrient uptake by cannabis plants. This sequence allows growers to create a stable nutrient solution.
Electrical conductivity (EC) measures the concentration of dissolved salts, including nutrients, in the water and nutrient solution. To achieve the ideal EC level of 1.2 to 1.6 for cannabis cultivation in soil, coco coir, or rockwool, it’s important to adjust the EC of the nutrient solution accordingly.
To achieve the ideal pH level of 6.0 to 6.3 inside the growing medium (soil, coco coir, or rockwool), it’s essential to adjust the pH of the water and nutrient solution accordingly. The pH of the water and nutrient solution should be slightly lower than the target pH of the growing medium.
Here’s a general guideline for adjusting the PH and EC of the water and nutrient solution:
Soil:
EC level of water and nutrient solution: Aim for an EC level of around 1.2 to 1.4.
Soil typically has a higher buffering capacity compared to coco coir or rockwool, so a slightly lower EC in the nutrient solution ensures that salts do not accumulate excessively in the soil. This allows for a more gradual release of nutrients to the plants.Water and nutrient solution pH: Adjust the pH of the water and nutrient solution to around 6.3 to 6.5.
The slightly higher pH of the water and nutrient solution ensures that when it interacts with the soil, it will buffer down to the desired pH range of 6.0 to 6.3 inside the soil.
Coco Coir:
EC level of water and nutrient solution: Aim for an EC level of around 1.4 to 1.6.
Coco coir has a lower buffering capacity compared to soil, so a slightly higher EC in the nutrient solution helps provide sufficient nutrients to the plants without causing nutrient deficiencies or imbalances.
Water and nutrient solution pH: Adjust the pH of the water and nutrient solution to around 5.8 to 6.0.
Coco coir tends to have a slightly acidic pH, so a slightly lower pH in the water and nutrient solution helps balance it out and reach the desired pH range of 6.0 to 6.3 inside the coco coir medium.
Rockwool (Hydroponics):
EC level of water and nutrient solution: Aim for an EC level of around 1.2 to 1.4.
Rockwool is an inert medium with no nutrient buffering capacity, so it’s essential to provide the correct EC level in the nutrient solution to meet the plant’s needs. Aim for a slightly lower EC compared to coco coir to prevent nutrient buildup and ensure optimal nutrient uptake.
Water and nutrient solution pH: Adjust the pH of the water and nutrient solution to around 5.5 to 5.8.
Rockwool typically requires a lower pH compared to soil or coco coir, as it is an inert medium. This lower pH ensures that the nutrient solution maintains the target pH range of 6.0 to 6.3 when absorbed by the plant roots in the rockwool.
It’s important to note that these are general guidelines, and actual pH adjustments may vary depending on factors such as the specific characteristics of the growing medium, nutrient composition, and environmental conditions. Regular monitoring of pH levels in both the water/nutrient solution and the growing medium is crucial to ensure that the pH remains within the optimal range for healthy cannabis growth. Adjustments should be made as needed to maintain stable pH levels throughout the cultivation cycle.

Nutrient Lockout in Cannabis Cultivation
Understanding and Addressing Common Nutritional Deficiencies in Cannabis Cultivation





You must be logged in to post a comment.