PH and EC testing of soil
Comprehensive Guide to Testing pH and EC Levels in Soil for Optimal Cannabis Cultivation
Cultivating cannabis successfully requires careful attention to various environmental factors, and two critical parameters that directly impact plant health and growth are soil pH and electrical conductivity (EC). Monitoring and adjusting these factors are essential for ensuring the optimal nutrient uptake and overall well-being of your cannabis plants. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the importance of pH and EC in soil, explain the testing processes, and provide practical tips on how to interpret and adjust these levels to create an ideal growing environment for your cannabis plants.
Importance of Soil pH in Cannabis Cultivation
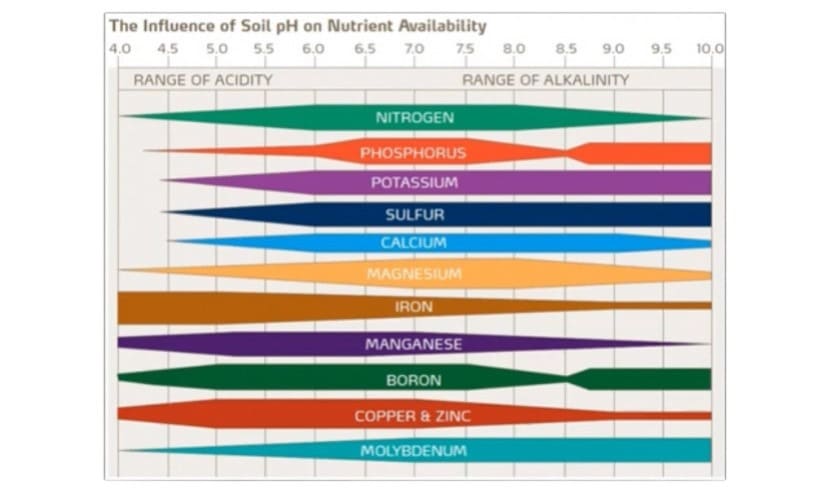
Soil pH is a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of the soil, influencing nutrient availability and microbial activity. Cannabis plants thrive in a slightly acidic to neutral pH range, typically between 6.0 and 7.0. When the pH deviates from this range, nutrient absorption can be compromised, leading to deficiencies or toxicities. Maintaining the correct pH level is crucial for optimizing nutrient uptake and promoting healthy plant development.
Importance of EC in Cannabis Cultivation
EC measures the concentration of dissolved salts in the soil, providing insights into nutrient levels. Cannabis plants require a balanced nutrient solution for healthy growth, and EC helps monitor the overall nutrient concentration in the soil solution. High or low EC levels can lead to nutrient imbalances, affecting plant health and productivity.
While pH and EC meters are commonly used tools for testing soil pH and electrical conductivity (EC), there are alternative methods that you can try if you don’t have access to these meters. Keep in mind that these methods may not be as accurate as using dedicated meters, but they can give you a rough idea of your soil conditions.
Testing Soil pH without pH meter:
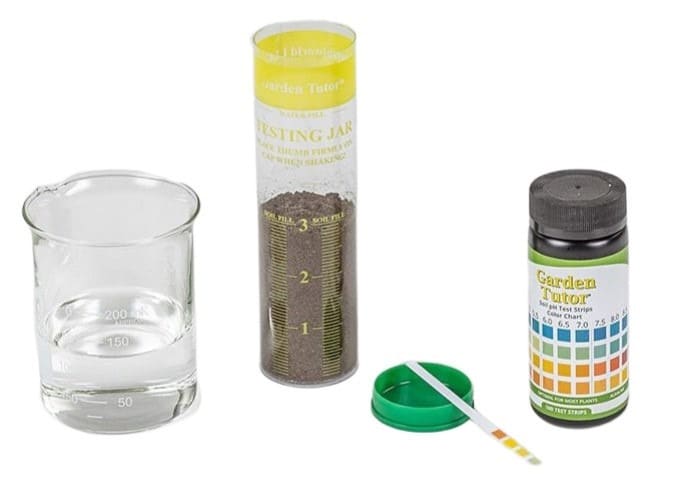
Strip Test Kits:
Strip test soil pH kits are convenient tools designed to measure the acidity or alkalinity of soil in a quick and straightforward manner. These kits typically include paper strips infused with pH-sensitive indicators. To use them, one simply inserts the strip into a soil sample, allowing it to react with the soil. After a specified time, the strip’s color is compared to a provided chart, indicating the soil’s pH level. Strip test soil pH kits are user-friendly and offer an affordable means of monitoring and managing soil health.
Red Cabbage Indicator:
Collect a handful of red cabbage leaves and chop them finely.
Boil the chopped leaves in water for about 10-15 minutes.
Strain the liquid and let it cool. This liquid will act as an indicator.
Mix a small amount of soil with the cabbage indicator.
If the mixture turns red, the soil is acidic. If it turns greenish, it’s neutral, and if it turns blue, it’s alkaline.
Vinegar and Baking Soda:
Mix a small amount of soil with distilled water to create a mud-like consistency.
Divide the mixture into two parts.
Add a small amount of vinegar to one part. If it fizzes, the soil is alkaline. If there’s no reaction, move to the next step.
To the other part, add baking soda. If it fizzes, the soil is acidic. If there’s no reaction, the soil is likely neutral.
Testing Soil pH using a pH meter
There are several methods to test soil pH, ranging from DIY home kits to professional laboratory analyses. For cannabis cultivation, a reliable and accurate pH meter is recommended. Follow these steps for accurate pH testing:
a. Select a representative soil sample from various areas of your growing space.
b. Use a pH meter calibrated specifically for soil testing.
c. Insert the probe into the soil at a depth of 6-8 inches.
d. Allow the meter to stabilize and record the pH reading.
Interpreting Soil pH Results
After obtaining the pH reading, interpret the results as follows:
a. pH 6.0-7.0: Optimal range for cannabis cultivation.
b. pH <6.0: Soil is acidic; consider adding lime to raise pH.
c. pH >7.0: Soil is alkaline; consider adding sulfur to lower pH.
Testing Soil EC without EC meter:
Salt Conductivity Test:
Dissolve a small amount of common table salt (sodium chloride) in distilled water until no more salt can dissolve.
Mix a small amount of soil with the saltwater solution.
If the solution conducts electricity, it indicates high electrical conductivity.
TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) Test:
Collect a soil sample and mix it with distilled water.
Let the mixture settle, and then pour off the liquid.
Evaporate the liquid, and the residue left behind will contain dissolved solids.
A higher amount of residue suggests higher EC.
Remember that these methods are not as accurate or precise as using dedicated meters, and the results may vary. For more accurate measurements, consider investing in a pH and EC meter for soil testing.Testing Soil EC with EC meter
Testing soil EC using an EC meter:
Accurate EC testing using an EC meter which measures the electrical conductivity of the soil solution. Follow these steps:
a. Collect a soil sample as described for pH testing.
b. Use an EC meter calibrated for soil testing.
c. Submerge the meter probe into the soil sample.
d. Record the EC reading after stabilization.
Interpreting Soil EC Results
Interpret EC results based on the growth stage and nutrient requirements of your cannabis plants:
a. Low EC (<1.0 mS/cm): Insufficient nutrients; consider adjusting nutrient solution.
b. Optimal EC (1.0-2.0 mS/cm): Suitable for most growth stages.
c. High EC (>2.0 mS/cm): Potential nutrient toxicity; dilute nutrient solution.
Adjusting Soil pH and EC
pH Adjustment
To modify soil pH, consider the following amendments:
a. To raise pH: Add agricultural lime according to package instructions.
b. To lower pH: Use elemental sulfur or acidic amendments like peat moss.
EC Adjustment
To adjust soil EC, modify your nutrient solution:
a. To increase EC: Add more concentrated nutrient solution.
b. To decrease EC: Dilute the nutrient solution with water.
pH and EC Monitoring Throughout the Growing Cycle
Seedling Stage
During the seedling stage, maintain a slightly lower pH (6.0-6.5) to facilitate nutrient absorption by young roots. Keep EC at a moderate level (0.8-1.2 mS/cm).
Vegetative Stage
In the vegetative stage, maintain pH within the optimal range (6.0-7.0) and gradually increase EC to support vigorous growth (1.2-1.8 mS/cm).
Flowering Stage
During the flowering stage, maintain pH within the optimal range (6.0-7.0) and adjust EC to support blooming plants (1.5-2.5 mS/cm).
Common Challenges and Troubleshooting
pH Fluctuations
Monitor pH regularly, as fluctuations can occur due to various factors. If pH drifts outside the optimal range, adjust accordingly using the recommended amendments.
EC Imbalances
Inconsistent EC levels may lead to nutrient imbalances. Regularly test and adjust nutrient solutions to ensure stable EC throughout the growing cycle.
Soil Composition
Understanding your soil’s composition is crucial for accurate pH and EC testing. Soil amendments and organic matter can influence readings, so consider periodic soil testing for a comprehensive analysis.
Achieving optimal soil pH and EC levels is vital for successful cannabis cultivation. Regular monitoring, accurate testing, and timely adjustments will create a stable and nutrient-rich environment, promoting healthy plant growth and maximizing yield. By following the guidelines outlined in this comprehensive guide, you can enhance your cannabis cultivation experience and cultivate robust, high-quality plants. Remember, each growing environment is unique, so adapt these recommendations based on your specific conditions for the best results.
Nutrient Lockout in Cannabis Cultivation











You must be logged in to post a comment.